Protected: Sitter Sheet
March 20, 2019
Pelvic Floor Exercises for Pregnancy
June 27, 2019Inflammation 101
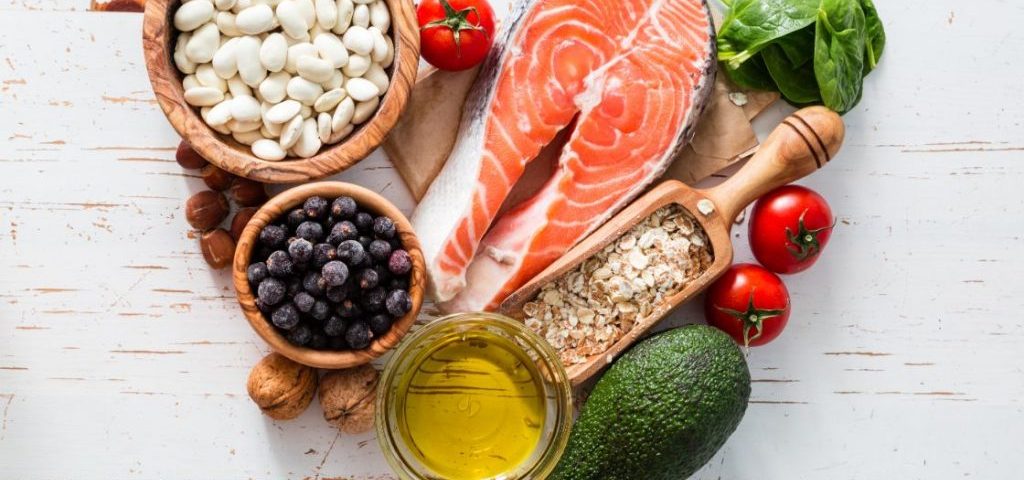
To give you a better understanding of the anti-inflammatory diet, let’s start with defining what inflammation is. Inflammation is a process by which the body’s white blood cells produce substances to protect the body from infection. When inflammation occurs, chemicals from white blood cells are released into the blood or affected area to protect the body from foreign invaders.

You can think of inflammation as the body’s attempt to heal itself. When something harmful or irritating affects a part of the body, there is a biological response to try to remove it. The signs and symptoms of inflammation, specifically acute inflammation include pain, heat, redness, swelling and/or loss of function.
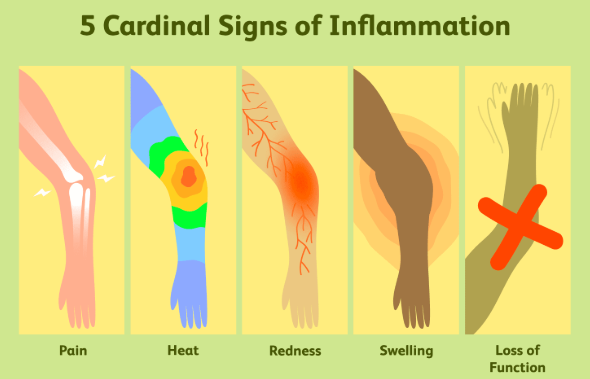
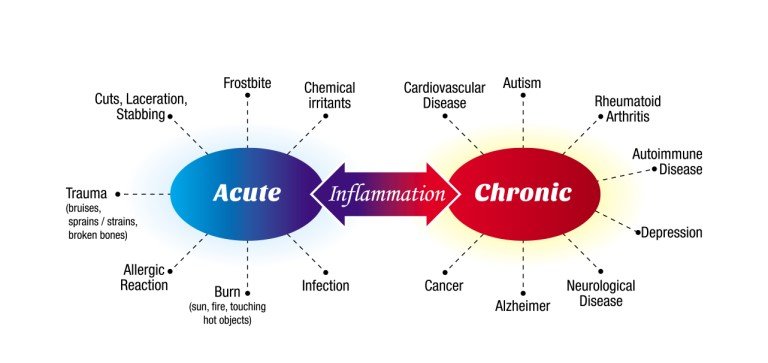
Most diseases stem from chronic (long-term) inflammation. Acute inflammation is the body’s immediate response at self-protection or healing. Chemicals are released from the damaged tissue to signal immune cells and hormones to fix the problem.
Chronic inflammation happens from a state of internal imbalance (stress, too much cortisol, lack of sleep, unhealthy diet) and can have a much slower but damaging effect on the body. This imbalance can signal the immune system to slowly release white blood cells which eventually build up and can start attacking internal organs and healthy tissue (specifically tissue in the gut). These cells can cause a plaque like buildup and DNA damage, leading to an increased risk of heart disease and cancer. Signs of chronic inflammation include body pain, especially in the joints, skin rashes such as eczema or psoriasis, low energy, poor digestion and autoimmune disorders.
Long-term inflammation can wreak havoc on the body and contribute to a weakened immune system and poor gut health. What’s interesting, is that 90% of the immune system lives in the gut. Research has found that there is a direct connection to the gut and the brain known as the gut brain connection. 90% of serotonin is actually made in the gut and plays a huge role in our mood, digestion and long-term happiness. Learn more about gut health and happiness here: https://kristenbrogan.com/hungry-for-happiness/
A High Sensitive C-Reactive Protein (HSC-RP) measures inflammation in the body. The best foods for improving HSC-RP levels are omega 3 fats, greens, water and alkaline foods and beverages. Your HSC-RP should be less than 1. About 1/3 of the adult population has elevated levels of HSC-RP. HSC-RP levels can also indicate an infection, or a chronic inflammatory disease, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, according to the Mayo Clinic. Learn more about inflammatory and autoimmune disease here: https://kristenbrogan.com/common-inflammatory-autoimmune-symptoms-issues/
What are the Key components of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?

Anti-inflammatory foods are those that can naturally lower inflammatory markers in the body. These foods can act as cox- 2 inhibitors that directly target an enzyme- like substance responsible for inflammation and pain. Food is typically your first line of defense and is said to be the most powerful medicine on the planet.
Antioxidant Rich Foods
Foods that naturally reduce inflammation are those that are rich in antioxidants; compounds that can inhibit oxidation and reduce free radicals (toxic byproducts) that can damage the cells in the body. Antioxidants are phytonutrients found in plant-based foods, specifically fruits, vegetables, and ancient grains. These foods are often referred to as superfoods or functional foods. Foods that are rich in color often contain the most antioxidants—think blueberries, strawberries, goji berries, broccoli, spinach, bell peppers, sweet potatoes, and lentils. Colorful spices like cinnamon, oregano, and turmeric are also rich in antioxidants, helping to reduce inflammation. You can find more antioxidant rich foods in the center two green circles of this Food Target.
Alkaline Rich Foods
Every food and beverage has an acid or alkaline characteristic and is measured on a pH scale of 0-14, with 0 the most acidic and 14 the most alkaline. Unfortunately, life in the United States can be extremely acidic. High levels of stress, poor sleep, processed foods, too much soda pop, coffee and alcohol can all make the body too acidic—causing it to use its valuable minerals such as calcium, iodine, and magnesium to bring the pH back into balance. Eating too much protein can also make the body extremely acidic since proteins are amino acids. (Too many amino acids = an acidic environment and acidic environments are where inflammation lives and thrives.
Whether a food or beverage is classified as acidic or alkaline is based on the effect they have on the body after digestion, end product of digestion. Apple cider vinegar, lemons, and limes are all acidic by nature but are alkaline once consumed. Alkaline rich foods (see pH chart) improve digestion, help to balance the gut flora, and lower inflammation in the body. You can test your pH of your saliva by using pH strips found at your local health food store or online.
Common problems associated with pH imbalance include acid reflux, poor digestion, chronic inflammation, headaches, poor bone health high blood pressure, low thyroid, muscle cramps, insomnia, fatigue, weight gain, and poor skin. Consuming more alkaline rich foods and beverages (see chart below) can help to bring your pH back into balance, naturally reducing inflammation. Learn more about balancing your pH with this informative video—How Diet Soda Causes Weight Gain.
Omega 3 Fats
Omega 3 fats like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and fish oil are some of the most powerful anti-inflammatory rich foods. These foods naturally reduce inflammation and improve cellular function and are especially helpful for reducing joint pain, stiffness and swelling associated with arthritis (inflammation of the joints). As a Dietitian, I recommend everyone consume a high-quality cod liver which is extremely rich in omega 3s such as DHA and EPA along with being high in naturally occurring vitamin D.
Chlorophyll Rich Foods
Chlorophyll rich foods are those that contain a deep green color (particularly green veggies and algae). Chlorophyll rich foods are naturally detoxifying, cleansing, energizing, and anti-inflammatory. They are also extremely rich in antioxidants and help to boost the immune system, protecting against inflammation and foreign invaders. As a Dietitian, I also recommend everyone consume high quality forms of chlorophyll such as spirulina/chlorella, a fresh water algae and wheatgrass, a mineral rich sprouted grass from the wheatberry.
Live Foods
Dead foods are foods that come in a box or a package and contain absolutely no live, digestive enzymes, which are needed to breakdown and absorb the food we eat. These are foods that can stay on the supermarket shelves forever. Live foods on the other hand, are those that contain live digestive enzymes, pre and probiotics needed to breakdown and absorb the food we eat. They naturally help to balance gut bacteria, boost the immune system and lower inflammation in the body. These are foods that will rot if we let them (fruits and vegetables). Aim for choosing foods as close to the source (natural state) as possible. Example: apple versus apple juice.
What are the Key Lifestyle Components of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
While an anti-inflammatory diet can be extremely helpful at lowering inflammation, it’s our overall lifestyle that can have the biggest benefit and greatest protection against disease. Keep in mind that inflammation happens when free radicals in the body out number the antioxidants, leading to a state of imbalance known as oxidative stress. This is why it’s important to look at your lifestyle as a whole, not just the foods you’re consuming.
Lifestyle factors that can cause inflammation are poor sleep, high stress, lack of movement, smoking, and long-term use of antibiotics and medications’ on top of consuming processed foods and beverages.
At On Target Living, we teach people how to live a balanced lifestyle that incorporates resting, eating, and moving practices. We provide speaking engagements to corporations to expand their people’s human capacity to do more, have more, and give more and have a proven system for doing so. We help organizations make health a business strategy since it’s our health that is our greatest competitive advantage.
When it comes to food, we specifically teach people how to eat alkaline rich and anti-inflammatory foods for better health and use this Food Target as our eating guide: https://ontargetliving.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/11/Food-Target-Updated1.pdf
We also provide many anti-inflammatory recipes in our best-selling cookbook, Target To Table: Healthy & Delicious Meals One Superfood at a Time. Some of our favorite anti-inflammatory recipes include our Mint Chocolate Chip Smoothie, Superfood Salad, and Fruitilicious Upside Down Cake.
What is the Difference between Whole30, a Mediterranean Diet, and an Anti-Inflammatory Diet?
While the Whole30 and Mediterranean Diet include some of the same qualities as the anti-inflammatory diet, there are some noticeable differences that make the anti-inflammatory diet stand out above the rest. The Anti-Inflammatory Diet can be thought of as more of a lifestyle that goes beyond just food. It’s a practice of finding more balance by incorporating rest and rejuvenation practices, daily movement, and nutrient rich foods with no food being off limits as long as it’s close to the source and in its most natural state. It’s also not as restrictive as other diets that aren’t sustainable long-term.

To recap, foods that naturally help to lower inflammatory markers in the body include:
- Antioxidant rich foods:
- Colorful fruits and vegetables
- Red and purple potatoes
- Sweet potatoes and yams
- Red and green lentils
- Ancient grains such as farro, amaranth, millet, quinoa, teff, sorghum, buckwheat, spelt, oats, black rice, wild rice
- Functional foods that offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition, promote optimal health and support disease prevention:
- Fermented foods (kefir, kimchi, sauerkraut, kombucha, miso, yogurt, pickled vegetables)
- Omega 3 fats (Fatty fish, chia seeds, flax seeds, walnuts)
- Hemp seeds
- Algae (spirulina, chlorella)
- Chlorophyll
- Wheatgrass
- Avocado
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Cacao
- Coconut oil
- Ghee
- Grass fed meats
- Wild game meats
- Beans
- Nut butters
- Alkaline rich foods (foods that are alkalizing upon digestion)
- Apple cider vinegar
- Mineral water (San Pellegrino, Gerolsteiner, Badoit)
- Ionized water
- Lemons, limes
- Leafy greens
- Sea vegetables
- Cinnamon
- Peppermint
- Nut milks
- Omega 6 fats high in gamma- linolenic acid (pumpkin seeds, hemp seeds, Brazil nuts, evening primrose oil)
- Other key components of an anti-inflammatory lifestyle include:
- 7-9 hours of sleep/night
- Meditation
- Deep breathing
- Epsom salt baths
- White space (planned down time that makes us human)
- Exercise
- Yoga
- Stretching
- Play (recreation activities)
- Time in nature
Science Based Sources Supporting an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- National Institute of Health
- Clevland Clinic
- Mayo Clinic
- Webmd
- CDC
- Chemistry of Man





