A Mindful Pregnancy
August 24, 2018
5 Simple Tips for Your Best Pregnancy
August 26, 2018Mindful Eater In Utero
Did you know that human’s development majority of their taste buds in utero? By week 20, your baby has already developed its taste buds and is learning to prefer the foods you eat. You can actually shape a baby’s palate by eating a variety of healthy foods. Bring on the broccoli!
In the third trimester they have more taste buds than they will in their entire lifetime. This is why it’s important to experiment with lots of new foods and put an emphasis on eating nutrient-rich foods during pregnancy that your baby will love as they age.
Research shows that pregnant Moms who eat junk food during pregnancy, will have kids who are more prone to eating junk food as they age.
Mindful Eating During Pregnancy
Food plays a huge role during pregnancy. It’s important to be mindful of how much and how often you indulge and understand when to give in to cravings. Eating a well-balanced diet full of lean meats, fruits, vegetables, ancient grains, and healthy fats will keep you feeling satisfied and will prevent overeating or food cravings during pregnancy. When your body feels nourished from nutrient rich foods, the less likely you are to have cravings. Adequate sleep is also important to get during pregnancy as it can help to keep your fat-storing, hunger, and satiety hormones balanced.
So many women I know before pregnancy are following strict diets like paleo and keto. What happens when they get pregnant is they immediately stop following these diets. Why? Because it’s not healthy for Mom or baby to restrict specific foods groups or carbohydrates that provide energy, antioxidants, and B vitamins. So, if you can’t follow a diet when you are pregnant, a time where you should be getting the best quality nutrition, why follow it otherwise? When you eat real foods, the body knows what to do. Oatmeal is not making us fat and restricting our carbohydrates will never make us happy or satisfied.
Pregnancy 101: Super Nutrients for Pregnancy
Before, during and after pregnancy it is important to eat a well-balanced diet consisting of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and calcium-rich foods. A healthy diet prior to pregnancy ensures that you have the nutrients you need to meet the needs of your growing baby.
Before Pregnancy:
Folate is a B vitamin that helps to prevent neural tube defects, serious abnormalities of the brain and spinal cord, which develops within the first month of pregnancy. Lack of folate during pregnancy may also increase the risk of low birth weight and preterm delivery. It is important to get 600-800 micrograms of folate or folic acid a day before conception and throughout pregnancy.
In addition to making healthy food choices, adding specific pre-natal superfoods or a daily prenatal vitamin– ideally starting three months before conception – can help ensure you’re getting enough of this essential nutrient.
*Recommended Daily Pre-Natal Superfoods: On Target Living Wheatgrass (4 cubes) & Spirulina/Chlorella (20 tablets), 1 tbsp cod liver oil
*I don’t typically recommend a pre-natal vitamin if you are doing the above superfoods. Combined, these superfoods will provide you with everything you need to grow a healthy baby and keep your immune system healthy. The greens like spirulina/chlorella and wheatgrass will be loaded with essential B vitamins like folate and cod liver oil will be a good source of omega 3 fats and vitamin A.
DHA & EPA are a type of Omega 3 fat found in cold-water fish that is linked to brain health and development. Since a baby’s brain starts forming in week 3 and continues all the way into week 40, it is important to supplement with omega 3s prior to pregnancy and during pregnancy. DHA is a major building block of tissue in the brain and retina of the eye and is extremely important during fetal development. EPA is important for infants, as it helps in the development of the cardiac and circulatory systems, improving brain function and blood flow. EPA also helps to balance hormones and promote a healthy immune system.
Although plant-based omega-3 fatty acids like flaxseeds and chia seeds are a great addition to the diet, they are poorly converted to EPA and DHA. However, these super seeds are a great source of ALA (alpha Linolenic Acid) and contain lignans, which have antiviral, antifungal, antibacterial, and anticancer properties. Flaxseeds also decrease inflammation, help lower cholesterol and improve cell sensitivity.
It is important to continue supplementation of DHA & EPA after pregnancy for optimal mental performance and improving memory, mood, and energy. It can also be taken to enhance the quality of breast milk.
In order to meet the omega 3 needs in the diet, pregnant women are left with essentially 2 choices: fish oil supplements supplying EPA and DHA (ideal source) or an algae-derived DHA for vegans/vegetarians.
| Servings/Day | DHA/EPA (mg) | Vitamin A (mcg) | Vitamin D (IU) |
| On Target Living Cod Liver Oil (1 tbsp) | 1275/1275 | 2,430 | 540 |
| Nordic Naturals Liquid Algae Omega- 3 (1.5 ml) drops | 1050/600 | Low Content | Low Content |
Daily Needs:
1,000-1,500 mg of DHA
800-1600 mg of EPA
Tolerable Upper Limit (Max Dose) Vitamin A: 2800 mcg
*Mercury in fish oil is very minimal due to the fact that mercury binds to protein (such as in fish meat) and not to the oil or the fatty part of the fish)
During Pregnancy:
During Pregnancy and into nursing, your needs increase for several vitamins and minerals in order to meet your increased needs as well as those of your growing baby. This is especially true for folic acid, choline, B12, iron, vitamin C, and protein. It is also important to consume adequate amounts of vitamin D to help with calcium absorption, bone development and promote a regular heartbeat and normal muscle function. Even though your nutrient needs increase during pregnancy, energy requirements only increase about 300 calories per day during the second and third trimester of pregnancy.
Best Sources of Folate
| Food | Serving | Amount of Folate (mcg) |
| Lentils | 1 cup (cooked) | 358 |
| Pinto Beans | 1 cup (cooked) | 300 |
| Chickpeas | 1 cup (cooked) | 280 |
| Spinach | 1 cup (cooked) | 265 |
| Black Beans | 1 cup (cooked) | 250 |
| Fortified Cereal | 1 cup | 400-800 (folic acid) |
| Sunflower Seeds | 1 ½ ounces | 101 |
| Avocado | ½ cup | 100 |
| Asparagus | 4 spears, cooked | 89 |
| Broccoli, collard greens | ½ cup, cooked | 84 |
| Chia, hemp, flax | ¼ cup | 50 |
| Brussels sprouts | ½ cup, cooked | 47 |
| Egg yolk | 1 egg | 25 |
| Oats | 1 cup | 25 |
| Wheatgrass | 4 ice cubes | 17 |
| Spirulina/Chlorella | 12 tablets | 15 |
Best Food Groups: Fortified cereals, leafy green vegetables, wheatgrass, citrus fruits, dried beans and peas.
*The synthetic form of folate found in supplements and fortified foods is known as folic acid.
Daily Needs:
Pregnancy 600-800 mcg
Nursing 500 mcg
Benefits: Folate helps prevent serious birth defects of a baby’s brain and spine.
Best Sources of Choline
| Food | Serving | Amount of Choline (mg) |
| Egg (found in the yolk) | 1 large (cooked) | 125 |
| Cod | 3 oz. (cooked) | 84 |
| Ground Beef | 3 oz. (cooked) | 83 |
| Pork Tenderloin | 3 oz. (cooked) | 76 |
| Shrimp | 3 oz. (cooked) | 69 |
| Salmon | 3 oz. (cooked) | 65 |
| Chicken | 3 oz. (cooked) | 65 |
| Wheatgrass | 4 cubes | 53 |
| Broccoli or Cauliflower | 1 ¼ cups (cooked) | 40 |
| Wheat Germ | 2 tbsp. | 21 |
Best Food Groups: Eggs, Meat, Seafood, and some whole grains.
*It is best to get choline from real foods since most dietary supplements supply little or no choline.
Daily Needs:
Pregnancy 450 mg
Nursing 550 mg
Benefits: Choline helps brain cells develop properly and has been shown to have long-lasting effects on a baby’s ability to learn and remember. Choline can also boost brainpower and increase mental focus during pregnancy. Choline works in tandem with folic acid to promote proper nervous system development during pregnancy.
Best Sources of Vitamin B12
| Food | Serving | Amount of Vitamin B12 (mcg) |
| Beef Liver | 3 oz. | 71 |
| Clams | 3 oz. | 16 |
| Crab | 3 oz. | 10 |
| Sardines | 3 oz. | 8 |
| Oysters | 3 oz. | 7 |
| Spirulina/Chlorella (Algae) | 12 tablets | 6.6 |
| Sockeye Salmon | 3 oz. | 6 |
Best Food Groups: Animal products, including fish, meat, poultry, eggs, milk and milk products. Vegan sources include fortified grains and nutritional yeast.
Daily Needs:
Pregnancy 2.2 mcg
Nursing 2.4 mcg
Benefits: Vitamin B12 is required for proper red blood cell formation to prevent anemia. It has also been shown to help with depression, memory loss, and improve overall brain health.
Best Sources of Vitamin C
| Food | Serving | Amount of Vitamin C (mg) |
| Red Peppers | 1 cup (raw) | 200 |
| Kiwi | 1 cup | 165 |
| Orange Juice | 1 cup | 125 |
| Green Peppers | 1 cup (raw) | 100 |
| Broccoli | 1 cup (cooked) | 100 |
| Strawberries | 1 cup | 100 |
| Spirulina/Chlorella | 12 tablets | 34-50 |
| Wheatgrass | 4 ice cubes | 3 |
Best Food Groups: Plant based milks, green vegetables, soybeans, fish, nuts, and seeds
Daily Needs:
Pregnancy 85mg
Nursing 120 mg
Benefits: Foods rich in vitamin C help with wound healing, tooth and bone development, and promotes metabolic processes.
Best Sources of Vitamin D
| Food | Serving | Amount of Vitamin D (IU) |
| Cod Liver Oil (On Target Living Brand) | 1 tbsp. | 540 |
| Salmon (sockeye) | 3 ounces | 447 |
| Tuna (canned in water) | 3 ounces | 154 |
| Fortified Milk | 1 cup | 150 |
| Mushrooms | 1 cup (raw) | 133 |
| Shrimp | 3 ounces | 110 |
| Egg Yolk | 1 Egg | 100 |
5-10 minutes Sunlight (during summer months) – 1000 IU
35 minutes Sunlight (during winter months) – 1000 IU
*Anything over 8 SPF blocks skin from absorbing vitamin D
Best Food Groups: Fatty fish, meat, mushrooms and eggs
Daily Needs for Vitamin D
Pregnancy 800-1,000 IU
Nursing 600-800 IU
Benefits: Vitamin D helps with calcium absorption, bone development and promotes a regular heartbeat and normal muscle function.
Best Sources of Iron
| Food | Serving | Amount of Iron (mg) |
| Soybeans | 1 cup (cooked) | 9 |
| White Beans | 1 cup (cooked) | 8 |
| Lentils | 1 cup (cooked) | 7 |
| Spinach | 1 cup (cooked) | 6 |
| Kidney Beans | 1 cup (cooked) | 5 |
| Artichokes | 1 cup | 5 |
| Dark Poultry Meats | 3 oz. | 2 |
Best Food Groups: Meat, seafood, beans, fortified cereals, leafy green vegetables.
Daily Needs:
Pregnancy 27 mg
Nursing 8 mg
Benefits: Iron is vital to the production of hemoglobin, the part of the red blood cell that carries oxygen to the cells in your body and your child’s body. Iron also plays a role in building a healthy immune system, enhances energy production, and helps development of a child’s brain and nervous system.
Best Sources of Calcium
| Food | Serving | Amount of Calcium (mg) |
| Collard Greens | 1 cup (cooked) | 320 |
| Greek Yogurt | 1 cup | 270 |
| Spinach | 1 cup (cooked) | 250 |
| Pinto Beans | 1 cup (Raw) | 218 |
| Black Eyed Peas | 1 cup (cooked) | 210 |
| Cheese | 1 ounce | 200 |
| Blackstrap Molasses | 1 tbsp. | 180 |
| Sesame Seeds/Tahini | 2 tbsp. | 180/50 |
| Mineral Water (High Mineral Content) | 2 cups | 170 |
| Chia Seeds | 2 tbsp. | 140 |
| Rhubarb | 1 cup (raw) | 110 |
| Fortified Milk | 1 cup | 100-450 |
| Kale | 1 cup (raw) | 100 |
| Canned Salmon (with bones) | 1 serving | 100 |
| Soybeans | ½ cup shelled | 80 |
| Figs | 2 dried figs | 80 |
| Almonds | 1 ounce (24 almonds) | 75 |
| Flaxseeds | 2 tbsp. | 50 |
| Wheatgrass | 3 ice cubes | 945 |
| Spirulina/Chlorella | 12 tablets | 12 |
Best Food Groups: Plant based milks, green vegetables, soybeans, fish, nuts and seeds
Daily Needs:
Pregnancy 1,000-1,500 mg
Nursing 1,000 mg
Benefits: You and your baby need calcium for strong bones and teeth. Calcium also helps your circulatory, muscular and nervous systems run normally.
Best Sources of Protein
| Food | Serving | Amount of Protein (g) |
| Organic Chicken Breast | 3 oz. | 26 |
| Organic Lean Beef | 3 oz. | 22 |
| Salmon | 3 oz. | 22 |
| Greek Yogurt (Siggi’s Brand) | 1 cup | 12-15 |
| Lentils | 1 cup | 17 |
| Edamame | 2/3 cup | 10 |
| Hemp Seeds | 3 tbsp. | 10 |
| Pumpkin Seeds | ¼ cup | 9 |
| Rolled Oats | ½ cup | 7 |
| Peanut/Nut Butter | 2 tbsp. | 7 |
| Black Beans | ½ cup | 7 |
| Raw Revolution Bars | 1 bar | 7 |
| Egg | 1 | 6 |
| Avocados | 1 | 6 |
| Quinoa (Complete Protein) | ¼ cup dry | 6 |
| Almonds | ¼ cup | 6 |
| Broccoli | 1 stalk | 5 |
| Tempeh | 1 oz. | 5 |
| Potatoes/Sweet Potatoes | 1 cup (1 medium size) | 4 |
| Brown/Whole Grain Rice | ¼ cup dry | 4 |
| Sprouted Bread | 1 slice | 4 |
| Hummus | ¼ cup | 4 |
| Spirulina/Chlorella | 20 tablets | 3 |
Best Food Groups: Organic poultry, wild caught seafood, nuts, beans, grains
The Recommended Daily Allowance for protein is 46 grams a day for adult women but more may be needed during pregnancy.
Daily Needs:
Pregnancy ½ body weight (lbs.) in grams
Nursing 0.36 grams of protein per lb.
Benefits: Protein supports the production of new cells, enzymes, and hormones that regulate life. Protein during pregnancy helps your baby grow fully, develop hair, fingernails, skin, organs and contributes to a healthy birth weight and fluid balance.
Eating Tips for Pregnancy
Seafood can be part of a healthy diet
- Eat 8 to 12 ounces of seafood each week.
- Recommended sources: Shrimp, crab, canned light tuna (limit albacore tuna), salmon, Pollock, catfish, cod, and tilapia.
- Avoid fish that contains high levels of mercury such as tile fish, shark, swordfish, and king mackerel since they have high levels of mercury. Too much mercury could damage your baby’s developing nervous system. The bigger and older the fish, the more mercury it’s likely to contain.
- Avoid raw, or contaminated seafood.
Avoid undercooked meat, poultry and eggs
- During pregnancy, you’re at increased risk of bacterial food poisoning and it is important to cook meats using a thermometer and avoid processed meats like deli meats and hot dogs.
Avoid unpasteurized foods
- This includes cheeses such as brie, feta, blue cheese, etc. unless clearly labeled as being pasteurized or made with pasteurized milk.
- Although, some unpasteurized foods like wheatgrass outweigh the risks and can contribute to a strong immune system for Mom and Baby.
Avoid unwashed fruits and vegetables
- To eliminate any harmful bacteria, thoroughly wash all raw fruits and vegetables and cut away damaged portions. Avoid raw sprouts of any kind – including alfalfa, clover, radish and mung bean – or be sure to cook sprouts thoroughly.
Sprouted grains are usually recommended as safe as it is baked at low temperatures, preserving many of the natural enzymes.
Avoid large quantities of vitamin A
- Recommended intake of vitamin A during pregnancy is 770 mcg. 3,000 mcg is the upper limit as too much vitamin A can cause birth defects.
Avoid excess caffeine
- Caffeine can cross the placenta and affect your baby’s heart rate.
- Limit caffeine to less than 200 mg a day during pregnancy.
- 8 ounces of brewed coffee equals about 95 mg
- 8 ounces of brewed tea contains about 47 mg
- 12-ounces caffeinated soda contains about 20 mg
- Avoid high caffeinated teas such as black and green tea
Avoid Alcohol
- One drink isn’t likely to hurt your baby, but no level of alcohol has been proved safe during pregnancy. The safest bet is to avoid alcohol entirely.
- Mothers who drink alcohol have a higher risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Too much alcohol during pregnancy can result in fetal alcohol syndrome, which can cause facial deformities, heart problems, low birth weight and mental retardation. Even moderate drinking can impact your baby’s brain development.
Recommended weight gain during pregnancy: Underweight: 28 to 40 pounds, Normal weight: 25 to 35 pounds, Overweight: 15 to 25 pounds, Obese: 11 to 20 pounds.
- You should gain weight gradually during your pregnancy, with most of the weight gained in the last 3 months. Many doctors suggest women gain weight at the following rate: 1 to 4 pounds total during the first 3 months (first trimester), 2 to 4 pounds per month during the 4th to 9th months (second and third trimesters)
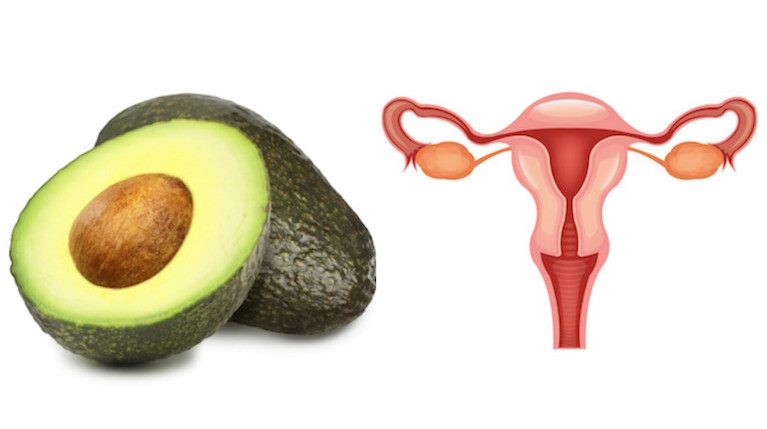
Avocados, Eggplant and Pears target the health and function of the womb and cervix, and help to balance hormones. Fun fact: These foods look just like the organs they target. It takes exactly 9 months to grow an avocado from blossom to ripened fruit.
Stay hydrated! Dehydration during pregnancy can cause early labor and delivery. If breastfeeding, aim for 13 cups of fluids daily. Drink more if you’re thirsty.
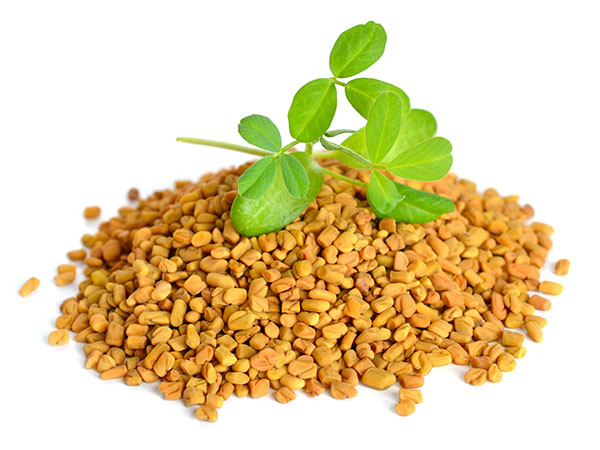
Fenugreek (herbal seed) naturally contains nutrients such as B vitamins, vitamin C, and Beta Carotene-all of which support the optimal production of breast milk. (Recommended by midwives)